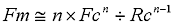Reliability Equations
Failure rates of modules
(constant failure rates)
Failure ratesThe number of failures of an item per unit time. May be observed failure rate (e.g. from 'returns' data); assessed failure rate (from tests) or extrapolated (from tests at higher stress levels). are a little like electrical resistances, there is a serial configuration (when the moduleA collection of hardware components that are more or less permanently connected. If a component in the module fails the complete module is replaced. fails if one of the component fails) and a parallel configuration (when all the members of some set of components have to fail for the module to fail).
The overall failure rate (Fm) for serial components is given by:
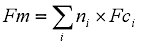 |
where Fci are the failure rates of the components and ni are the numbers of components. |
The failure rate (Fm) for parallel components is given by:
Note: there are many formulae for parallel redundancy depending on how/when failed components are repaired and how many working components are needed. The formulae above is the most optimistic and is the case when failed components are immediately repaired and only one is required.
Repair rates of modules
The overall repair rate (Rm) for serial components is given as a weighted average by:
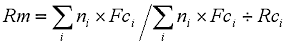
The overall repair rate (Rm) for n parallel components is given by:
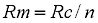
The reason for this slightly surprising result is that repair of the first failed component has already started when the last fails.
Availability of modules
The availabilityThe proportion of time that an item is capable of operating to specification within a large time interval. of a module or component is given by:
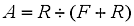
The unavailabilityThe propourtion of time that an item is incapable of operating to specification within a large time interval. Equals 1 - Availability. is simply 1-A.
The equations given on this page provide a first estimate of module and system reliability parameters, but contain a numerous approximations and assumptions.
Optimal Solutions welcomes enquiries on Reliability, and would be pleased to provide consultancy tailored to your requirements. You can get in touch by sending a message from our Contact Us page, or by calling us on the number below.