Reliability Calculations
System reliability can be calculated from the RBDA diagram that links the elements of a product that need to be working for the product to work. So long as there is a path from the start of the diagram to the end of the diagram the equipment can provide the service. The diagrams can be hierarchical so that blocks at one level can be decomposed into an RBD at a lower level. models quite easily provided that the following simplifying assumptions are valid:
- constant failure rate
- unlimited repair resources
- all failures revealedFailures that are immediately recognised, possibly by some monitoring system. The alternative is that the failure of modules may only be revealed during regular inspections. Unrevealed failures result in less protection by redundancy since on average the item will be unavailable for half the inspection period for each failure.
- independent failureIndependent failure is when items do not fail by a common cause, but fail through random normally unknown causes. of components and modules
- sufficiently simple RBD.
Sufficiently simple means that the RBD can be decomposed into a sequence of or connections after and connections have been accumulated, but please contact us for clarification about 'sufficiently simple'.
If the assumptions above are valid, the probability that a module is working at an instant is given by the availabilityThe proportion of time that an item is capable of operating to specification within a large time interval. of the module. The rules for combining probabilities then give the following equations:
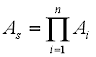 and
and
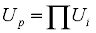 together with
together with
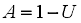
|
where As is the availability of serial blocks and Up is the unavailabilityThe propourtion of time that an item is incapable of operating to specification within a large time interval. Equals 1 - Availability. of parallel blocks.
These calculations can be conveniently organised on a spreadsheet. The repair rateThe number of corrective maintenance actions that can be carried out in unit time. Corrective action should also include logistic allowance, diagnosis time, and time needed to bring the equipment fully back on line, unless some of these activities are considered elsewhere in calculations.. for the system has to be calculated before the failure rateThe number of failures of an item per unit time. May be observed failure rate (e.g. from 'returns' data); assessed failure rate (from tests) or extrapolated (from tests at higher stress levels). for the system can be estimated from the system availability. This should use the equations given in the Reliability Equations section.
When the simplifying assumptions do not apply more powerful methods are needed to calculate the overall reliabilities from the diagrams. Markov models can deal with more realistic repair assumptions but require considerable mathematical expertise. Reliability simulation models require few prior assumptions but may require long running times to get accurate predictions for highly reliable systems.
Optimal Solutions have considerable experience in developing reliability models, and welcome enquiries on Reliability. We would be pleased to provide consultancy tailored to your requirements. You can get in touch by sending a message from our Contact Us page, or by calling us on the number below.