Linear Programming Model Formulation
Linear programming fits the optimisation paradigm of model, constraints and cost function as shown below. However since all the relationships are linear the three parts, model; constraints; and cost function, can be condensed into a common format.
Linear Optimisation
| For decision variables: | 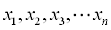 |
| Model constants: | 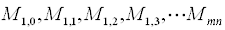 |
| Constraints constants: | 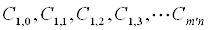 |
| Cost function constants: | 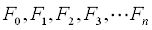 |
| and with the right hand side of the model and constraints being: | |
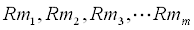 and
and
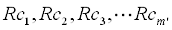
|
|
The model is given by the equations:
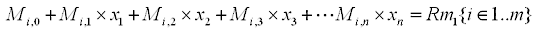
the constraints are:
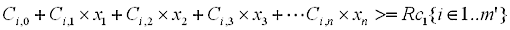
and the cost function is:
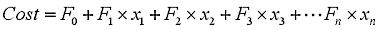
The general problem is minimise the Cost subject the model equations and the constraints.
With most LP tools it is usually possible to also specify constraints using the '<=' operator. In a similar way the '=' of the model and cost function is also an operator so that all aspects of the problem can be considered as constraints.
In practice to aid understanding of the problem and to avoid minimising negative quantities, LP tools also support maximising the cost function. In this case 'cost' is more properly thought of as profit.
MPS format
There is an industry standard method for describing Linear Programming problems in text files. This standard is known as MPS format. Most good quality LP tools support this format. The file format has the following sections: NAME, ROWS, COLUMNS, RHS, RANGES, BOUNDS and ENDATA.
Optimal Solutions welcomes enquiries on Linear Programming, and would be pleased to offer consultancy on this, or any other aspect of Optimisation. You can get in touch by sending a message from our Contact Us page, or by calling us on the number below.